Blockchain technology has revolutionized how we think about digital transactions and decentralized networks.
At the heart of every blockchain is a critical component known as the genesis block.
Understanding the genesis block helps us grasp the fundamentals of how blockchains operate and why they are so secure and innovative.
What is a Genesis Block?
The genesis block is the very first block of a blockchain, serving as the foundation upon which all subsequent blocks are built.
Think of it as the cornerstone of a building – without it, nothing else can stand.
This initial block is essential because it provides the starting point for the entire blockchain network. It’s an anchor, establishing the initial parameters and conditions for the network.
Proof of Work vs. Proof of Stake
Blockchains can operate using different consensus mechanisms, with the two most common being Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS).
In PoW blockchains, such as Bitcoin, miners must perform a certain amount of computational work to create new blocks.
This involves solving complex mathematical problems, which requires significant processing power and energy.
The genesis block in a PoW system is no exception; miners must also complete work to establish it. This ensures that the network starts on a secure footing, with a verifiable and tamper-proof block.
In contrast, PoS networks operate differently. Instead of requiring miners to perform extensive computations, these networks rely on validators who are chosen based on their stake, or ownership, in the network.
The genesis block in PoS systems is typically pre-created by the developers, setting the stage for the network to operate smoothly from the beginning.
The Role and Importance of Genesis Blocks
The genesis block is crucial because it provides a reference point for all subsequent blocks in the blockchain. Each block in the chain links back to the previous one, creating an unbroken and tamper-resistant record of transactions.
This linking is fundamental to the blockchain’s security, as altering any single block would require changing all subsequent blocks, which is practically impossible due to the computational power required.
Furthermore, the genesis block establishes key initial parameters for the network.
These parameters can include the mining difficulty, which dictates how challenging it is to create new blocks, and the block reward, which is the incentive given to miners or validators for adding new blocks to the chain.
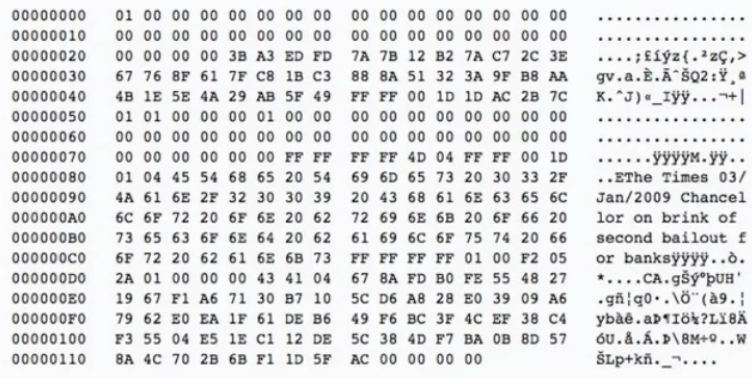
Bitcoin’s Genesis Block
Bitcoin, the first and most well-known cryptocurrency, was launched with its genesis block created by the network’s mysterious and anonymous developer, Satoshi Nakamoto, on January 3, 2009.
This block is particularly famous not only for being the foundation of Bitcoin but also for the special message it contains.
Embedded in the genesis block is the title of a newspaper article from that day’s issue of
The Times: “The Times 03/Jan/2009 Chancellor on brink of second bailout for banks.”
This message is widely interpreted as a critique of the traditional banking system and a nod to the motivations behind Bitcoin’s creation.
Many believe that Satoshi Nakamoto was inspired by the financial crisis of 2008 and the subsequent bank bailouts, which highlighted the vulnerabilities and ethical failings of the centralized financial system.
The reward for mining Bitcoin’s first block was 50 bitcoins, but this amount cannot be spent. This reward system is built into Bitcoin’s code and is designed to halve approximately every four years, a process known as “halving.”
Eventually, the reward will reach zero around the year 2140, by which time all 21 million bitcoins will have been mined.
Genesis Blocks in Other Cryptocurrencies
Following Bitcoin’s success, many other cryptocurrencies adopted similar methods for creating their genesis blocks.
Ethereum, for example, initially used the PoW method but designed its genesis block to allow pre-launch access to cryptocurrencies for its owners and investors. This approach ensured a smooth public launch and established trust in the network.
Litecoin, another popular cryptocurrency, closely followed Bitcoin’s method for creating its genesis block. However, it introduced a few differences, such as using a different mining algorithm, Scrypt, which is designed to be more accessible to a wider range of miners.
Dogecoin, a cryptocurrency initially created as a joke, also paid homage to Bitcoin with its genesis block. It included a reference to a newspaper article about Bitcoin’s rising price, symbolically linking Dogecoin to its predecessor.
Symbolism and Common Features
Genesis blocks often carry symbolic messages or references, reflecting the values and motivations behind the creation of the cryptocurrency.
These messages can commemorate significant events or convey the ethos of the developers.
For example, Bitcoin’s reference to the bank bailout underscores its mission to offer an alternative to the traditional financial system.
Despite differences in implementation, genesis blocks share common features.
They include essential information such as the timestamp, the hash value of the block, the hash value of the preceding block (which is zero for the genesis block), the nonce number, and the block reward.
In PoW systems, the nonce value is particularly important as it relates to the amount of computational work required to create the block.
Conclusion
The genesis block is a foundational element of any blockchain network. It serves as the starting point and anchor for all subsequent blocks, ensuring the integrity and security of the blockchain.
Whether created through PoW or PoS mechanisms, the genesis block sets the stage for the network’s operation and reflects the vision and motivations of its creators.
By understanding the genesis block, we gain insight into the core principles and innovations that make blockchain technology so powerful and transformative.
Have you read it yet? Terraform-SEC final agreement on the horizont
Disclosure:This article does not contain investment advice or recommendations. Every investment and trading move involves risk, and readers should conduct their own research when making a decision.
Kriptoworld.com accepts no liability for any errors in the articles or for any financial loss resulting from incorrect information.